Purpose
The purpose of implementing SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) is to enable organizations to make informed, data-driven decisions by providing a comprehensive analytics platform. SAP Analytics Cloud is a complete solution for analytics and planning that is designed to unlock the full potential of all your investments in mission-critical business applications and most valuable data sources. SAC integrates data from various sources, including SAP and non-SAP systems, into a single, unified view, allowing users to analyze and visualize data in real-time.
The Business Scenario and Objectives
The Business Scenario
Persona
You’re an intermediate business user employed at XYZ Company, also serving as an intermediate consultant. While you possess a solid understanding of SAP Analytics Cloud fundamental concepts, modeling, and story building, you’re relatively new to SAP Analytics Cloud Planning, particularly in the context of enterprise planning.
Recently, you’ve taken on a new assignment to implement SAP Analytics Cloud planning, working under the guidance of an experienced project lead. This role presents an opportunity for you to leverage your existing knowledge and skills while gaining valuable experience in SAP Analytics Cloud Planning.
Tasks to be Accomplished
Working alongside an experienced project lead, your role involves configuring planning models, data actions, allocations, and stories within SAP Analytics Cloud for planning purposes. These configurations facilitate various planning activities such as manual input planning, version management, planning simulations, allocations, data copying, labor and benefits calculations, currency translation, data input validation, sales forecasting, and job scheduling.
To effectively manage planning tasks, you’ll create a plan process in the calendar, ensuring each regional planner executes their designated activities. Once all regions have completed their planning and received approval, the plan data will be locked, allowing for the publication of results.
Overview to the Planning Process in SAP Analytics Cloud
Using the example of XYZ Company, we’ll take you through the planning process and the related functionality in SAP Analytics Cloud.
Ana, a planner at XYZ Company, is utilizing SAP Analytics Cloud Planning for preparing the income statement forecast. In the preparation phase, her team will configure models and planning objects to meet business requirements. During planning, they’ll leverage SAP Analytics Cloud for forecasting, analysis, and prediction, particularly valuing its integration with predictive and analytics features. Upon completing the forecast, they’ll utilize the calendar feature to monitor progress, approve, and finalize results.
The Preparation Phase
During the Preparation Phase, as the individual in charge of planning modeling, your primary tasks involve:
- Constructing planning models and defining dimensions to structure your planning data effectively.
- Incorporating planning objects, including data actions, to facilitate data manipulation and management within the planning environment.
- Developing stories tailored for planning purposes, enabling visualization and analysis of planning data.
- Establishing and assigning tasks and processes to streamline planning workflows and ensure efficient collaboration among team members.
The Planning Phase
As a planner, your key responsibilities during this phase include:
- Inputting relevant data into the plan, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
- Collaborating with stakeholders across various departments to incorporate their inputs and feedback into the plan.
- Making iterative changes to the plan as needed based on evolving requirements and feedback.
- Publishing the finalized data to make it accessible and transparent to all relevant stakeholders.
The Finalize Phase
As the planning process approaches its conclusion, the following steps are typically undertaken:
- Reviewing: The results of the planning process are thoroughly reviewed to ensure accuracy, completeness, and alignment with organizational goals and objectives.
- Approval: Once the results have been reviewed, they are submitted for approval by relevant stakeholders, such as department heads or executives, who validate the accuracy and relevance of the data.
- Publication: After approval, the finalized data is published to make it accessible to all relevant parties, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Locking: To maintain data integrity and prevent unauthorized changes, the approved data is locked, ensuring that it remains unchanged until the next planning cycle or review period.
SAP Analytics Cloud Planning Concepts
Summary of Key Concepts in SAP Analytics Cloud Used in Planning
The following table contains SAP Analytics Cloud concepts that are used in planning, as well as brief descriptions
| Planning Concept | Description |
| Connections |
|
| Dimensions |
|
| Planning models |
|
| Data imports |
|
| Data exports |
|
| Data locking | Used to protect data from changes. When planning data is approved, prevent data changes by setting a data lock for the planning version and period/year. |
| Data point comments | Plan data can be entered by base member or by hierarchy parent node. When data is entered by hierarchy parent node, the data is disaggregated to its children equally or in proportion to existing values. |
| Disaggregation | Plan data can be entered by base member or by hierarchy parent node. When data is entered by hierarchy parent node, the data is disaggregated to its children equally or in proportion to existing values. |
SAP Analytics Cloud Planning User Interfaces
Access Planning Options in SAP Analytics Cloud
Planning-related objects can be accessed from the Navigation Bar.
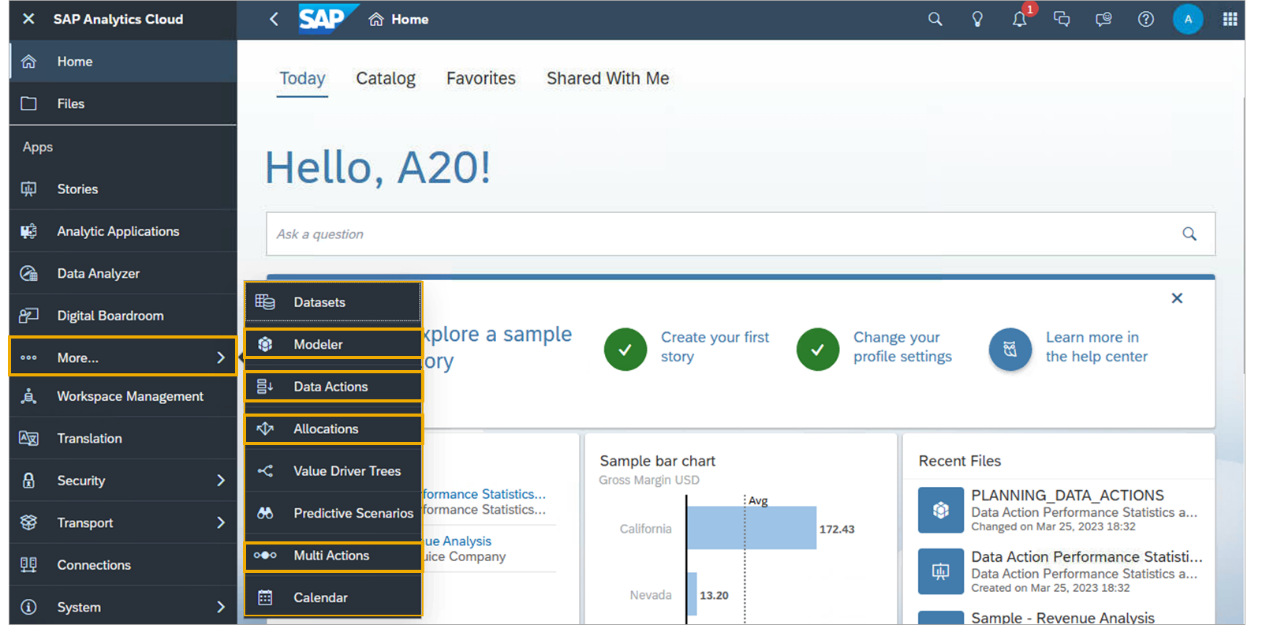
User Interfaces for Performing Planning Activities
You can perform planning activities in various user interfaces:
- Basic stories:
- Primary user interface
- Created and maintained by the business users

Extended, or scripted, stories:
- Used for more complex business requirements
- Created with developers and maintained by IT
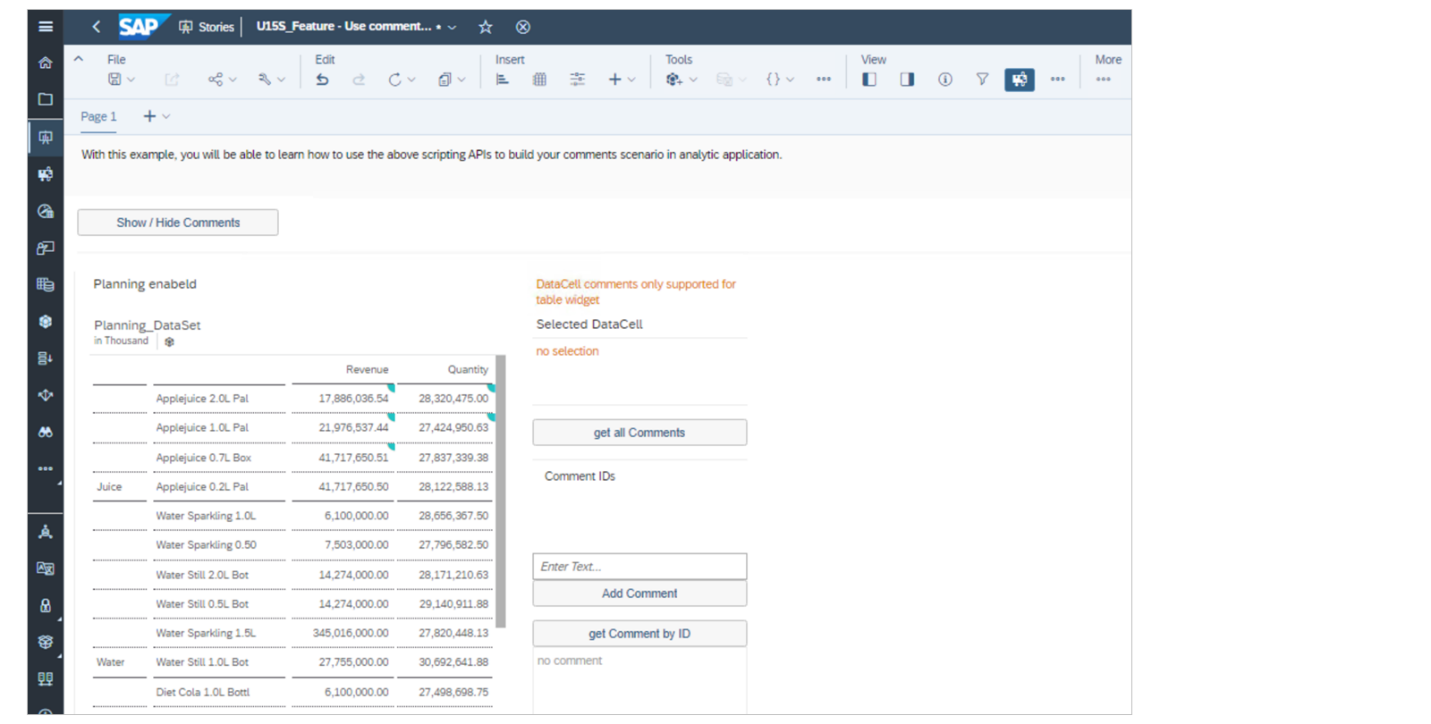
SAP Analytics Cloud, add-in for Microsoft Office:
- Microsoft Excel client
- Web Excel
- Maintained by the business users

SAP Analysis for Microsoft Office:
- Microsoft Excel client
- Maintained by the business users
- No further development for SAP Analytics Cloud integration

Use Basic Stories in Planning
In the following example, the SAP Finance: FP&A – Rapid Financial Planning and Analysis Landing Page story is displayed. This is just one example of planning content that is delivered with SAP Analytics Cloud.
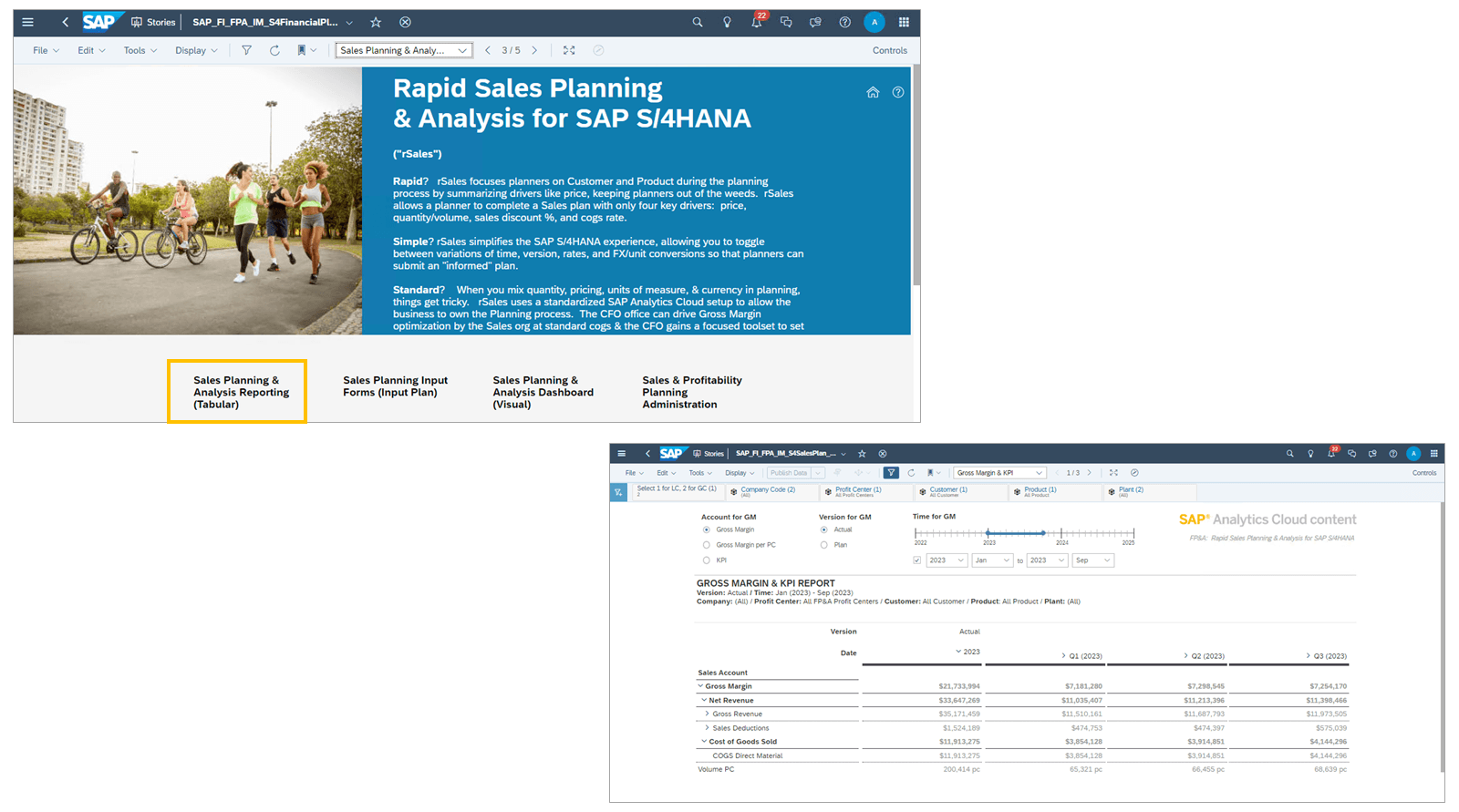
Stories are based on planning models. Each planning model works with several internal processes or functions but all have the same focus, to make planning work more efficiently.
Using stories in planning has the following advantages:
- One tool to strategize and react in the moment
- See the impact of your actions
- Collaborate with comments, discussions, and interactions
If a table is being used in a story for planning, then planning tool options are shown in the menu.
Page options either display in the …More options or in the task bar at the top of the page, depending on your screen resolution.
Use Tables in Planning
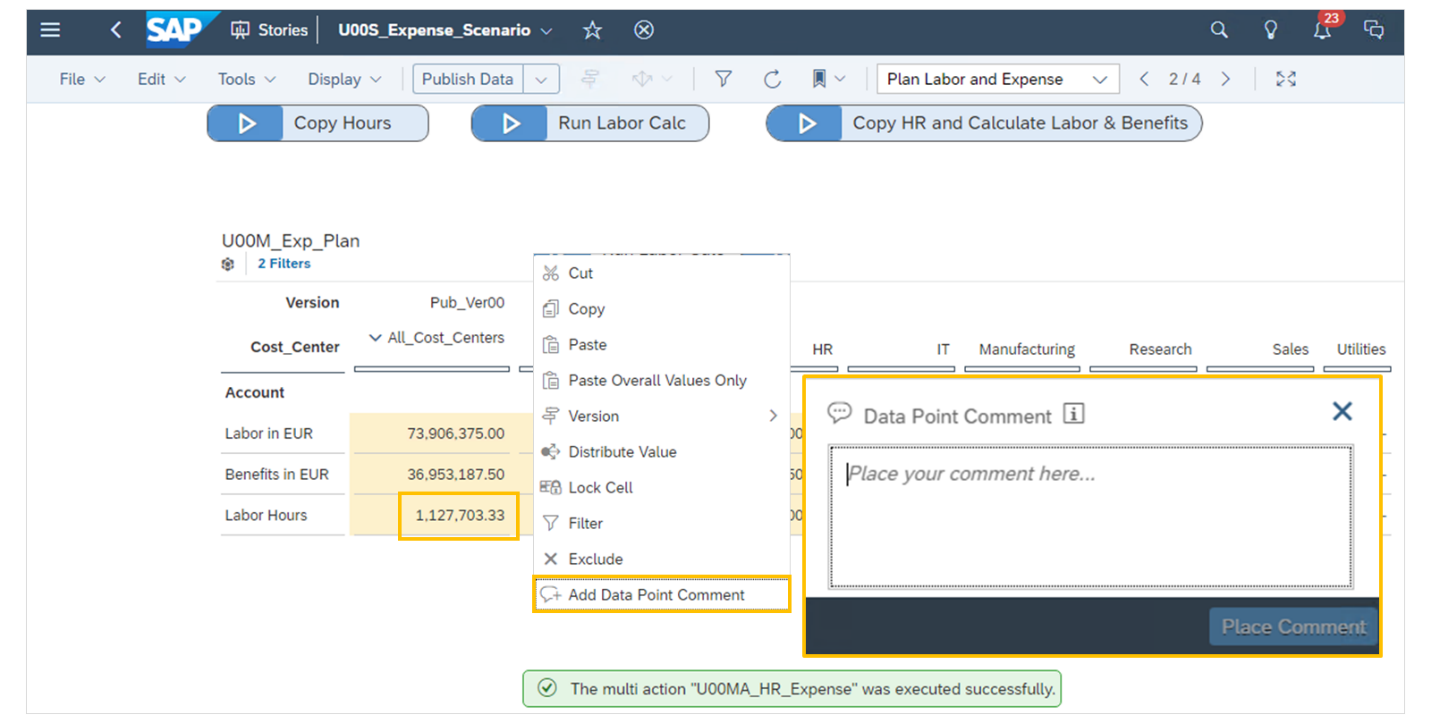
If a table is being used in a story for planning, then planning tool options are shown in the menu.
Page options either display in the …More options or in the task bar at the top of the page, depending on your screen resolution.

Note:
Your screen resolution affects where you access tasks in SAP Analytics Cloud. For example, Version Management appears in the task bar if you have a high resolution and won’t be available in the …More menu option or in the Tools …More option.
Reasons for Unplannable Data: When you hover over a cell that is secure or locked, for example, the tooltip appears on the upper right with the explanation.
Extended stories in SAP Analytics Cloud offer several advantages for planning:
- Supplementing the SAP Analytics Cloud planning experience in basic stories: Extended stories provide additional functionalities and customization options beyond basic stories, enhancing the planning experience for users.
- Creating highly dynamic and customized planning applications: With extended stories, analytic developers can build planning applications tailored to specific business requirements, incorporating advanced features and interactivity.
- Designing planning applications with minimal training effort: Extended stories allow for the creation of user-friendly planning applications that require minimal training for users to understand and navigate effectively.
Typical use cases for extended stories include:
- Form-based data input: Extended stories are ideal for implementing form-based data input interfaces, allowing users to input planning data in a structured and intuitive manner.
- Complex user interface requirements: When planning processes require sophisticated user interfaces with advanced functionalities, extended stories provide the flexibility to meet these requirements.
- Guided planning and approval workflows: Extended stories can support guided planning and approval workflows, helping users navigate through the planning process step-by-step and ensuring proper validation and approval of data.
- Bullet-proof and self-explaining applications: Extended stories enable the creation of planning applications that are robust, error-resistant, and self-explanatory, minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring data accuracy and integrity.
Summary: Stories vs Extended Stories in SAP Analytics Cloud
Stories are designed for self-service use cases, allowing users to create and customize visualizations for their analytics needs. In contrast, extended stories are developed by analytic professionals for more sophisticated and tailored applications.
Extended stories leverage charts, tables, and widgets configured in the Left Side Panel, with the flexibility to enhance their behavior and appearance using scripts. These scripts are executed based on user actions within the extended story, enabling interactivity and dynamic functionality.



